案例分析:重构“策略”模式
经典的“策略”模式
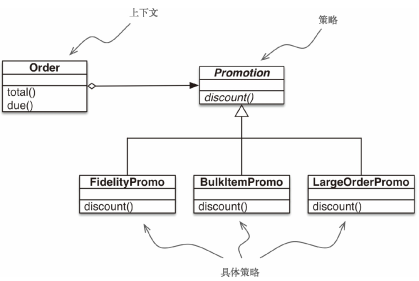
图中的UML类图指出了“策略”模式对类的编排。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106# classic_strategy.py
# Strategy pattern -- classic implementation
"""
# BEGIN CLASSIC_STRATEGY_TESTS
>>> joe = Customer('John Doe', 0) # <1>
>>> ann = Customer('Ann Smith', 1100)
>>> cart = [LineItem('banana', 4, .5), # <2>
... LineItem('apple', 10, 1.5),
... LineItem('watermellon', 5, 5.0)]
>>> Order(joe, cart, FidelityPromo()) # <3>
<Order total: 42.00 due: 42.00>
>>> Order(ann, cart, FidelityPromo()) # <4>
<Order total: 42.00 due: 39.90>
>>> banana_cart = [LineItem('banana', 30, .5), # <5>
... LineItem('apple', 10, 1.5)]
>>> Order(joe, banana_cart, BulkItemPromo()) # <6>
<Order total: 30.00 due: 28.50>
>>> long_order = [LineItem(str(item_code), 1, 1.0) # <7>
... for item_code in range(10)]
>>> Order(joe, long_order, LargeOrderPromo()) # <8>
<Order total: 10.00 due: 9.30>
>>> Order(joe, cart, LargeOrderPromo())
<Order total: 42.00 due: 42.00>
# END CLASSIC_STRATEGY_TESTS
"""
# BEGIN CLASSIC_STRATEGY
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
from collections import namedtuple
Customer = namedtuple('Customer', 'name fidelity')
class LineItem:
def __init__(self, product, quantity, price):
self.product = product
self.quantity = quantity
self.price = price
def total(self):
return self.price * self.quantity
class Order: # the Context
def __init__(self, customer, cart, promotion=None):
self.customer = customer
self.cart = list(cart)
self.promotion = promotion
def total(self):
if not hasattr(self, '__total'):
self.__total = sum(item.total() for item in self.cart)
return self.__total
def due(self):
if self.promotion is None:
discount = 0
else:
discount = self.promotion.discount(self)
return self.total() - discount
def __repr__(self):
fmt = '<Order total: {:.2f} due: {:.2f}>'
return fmt.format(self.total(), self.due())
class Promotion(ABC): # the Strategy: an Abstract Base Class
def discount(self, order):
"""Return discount as a positive dollar amount"""
class FidelityPromo(Promotion): # first Concrete Strategy
"""5% discount for customers with 1000 or more fidelity points"""
def discount(self, order):
return order.total() * .05 if order.customer.fidelity >= 1000 else 0
class BulkItemPromo(Promotion): # second Concrete Strategy
"""10% discount for each LineItem with 20 or more units"""
def discount(self, order):
discount = 0
for item in order.cart:
if item.quantity >= 20:
discount += item.total() * .1
return discount
class LargeOrderPromo(Promotion): # third Concrete Strategy
"""7% discount for orders with 10 or more distinct items"""
def discount(self, order):
distinct_items = {item.product for item in order.cart}
if len(distinct_items) >= 10:
return order.total() * .07
return 0
# END CLASSIC_STRATEGY
每个具体策略都是一个类,而且都只定义了一个方法,即discount。此外,策略实例没有状态(没有实例属性)。你可能会说,它们看起来像是普通的函数。以下示例是对以上示例的重构,把具体策略换成了简单的函数,而且去掉了Promo抽象类。
Order 类和使用函数实现的折扣策略
1 | # strategy.py |
best_promo 函数计算所有折扣, 并返回额度最大的
1 | # strategy_best.py |
找出模块中的全部策略
1 | # strategy_best2.py |

